In Microsoft SQL Server, functions are database objects that perform a specific task or computation.
Functions are stored permanantly in database and used for easy end user access and reports.
SQL Server provides various types of functions, including scalar functions, table-valued functions, and aggregate functions. Here are the main types of functions in SQL Server:
1. Scalar Value Returning Functions:
Scalar functions returns single value as the output.
- Built-in Scalar Functions:
- SQL Server provides a variety of built-in scalar functions that operate on a single value and return a single value.
Here’s a table presenting some commonly used built-in scalar functions in Microsoft SQL Server:
| Function category | Description |
|---|---|
| Configuration Functions | Return information about the current configuration. |
| Conversion Functions | Support data type casting and converting. |
| Cursor Functions | Return information about cursors. |
| Date and Time Data Types and Functions | Perform operations on a date and time input values and return string, numeric, or date and time values. |
| Graph Functions | Perform operations to convert to and from character representations of graph node and edge IDs. |
| JSON Functions | Validate, query, or change JSON data. |
| Logical Functions | Perform logical operations. |
| Mathematical Functions | Perform calculations based on input values provided as parameters to the functions, and return numeric values. |
| Metadata Functions | Return information about the database and database objects. |
| Security Functions | Return information about users and roles. |
| String Functions | Perform operations on a string (char or varchar) input value and return a string or numeric value. |
| System Functions | Perform operations and return information about values, objects, and settings in an instance of SQL Server. |
| System Statistical Functions | Return statistical information about the system. |
| Text and Image Functions | Perform operations on text or image input values or columns, and return information about the value. |
For a more detailed reference and to explore additional functions, refer to the official Microsoft documentation: Scalar Functions (Transact-SQL).
- User-Defined Scalar Functions:
- Users can create their own scalar functions to encapsulate custom logic. These functions can be used in SELECT, WHERE, and other clauses.
Syntax:
CREATE FUNCTION <FUNCTION_NAME>
(
-- Input parameters
@parameter1 data_type,
@parameter2 data_type,
-- ... (additional parameters if needed)
)
RETURNS return_data_type --any data type except table
AS
BEGIN
-- Function body
DECLARE @result return_data_type;
-- Custom logic here
-- SET Set the value of @result based on the input parameters and custom logic
RETURN @result;
END;
Example:
A simple example is to calculate sum of three numbers.
CREATE FUNCTION fnFindSum (@Input1 int, @Input2 int, @Input3 int)
RETURNS INT
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @SUM INT
SET @SUM = @Input1 + @Input2 + @Input3
RETURN (@SUM)
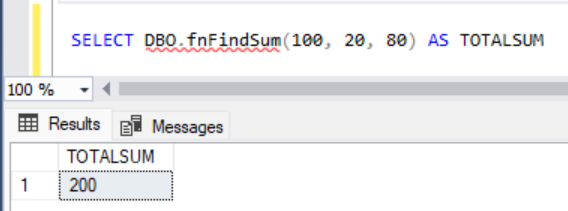
ENDThe above function has to be called with parameter as follows.
SELECT DBO.fnFindSum(100, 20, 80) AS TOTALSUMOutput:
2. Table-Valued Functions:
- Inline Table-Valued Functions (iTVF):
- These functions return a table-like result set and are typically used in the FROM clause of a SELECT statement.
- These functions store single statement in the function definition.
Syntax:
CREATE FUNCTION <FUNCTION_NAME>
(
-- Input parameters
@parameter1 data_type,
@parameter2 data_type,
-- ... (additional parameters if needed)
)
RETURNS TABLE
AS
RETURN
(
<<SELECT QUERY>> -- SELECT statement defining the function logic
);Example:
Let us create some sample tables for demonstration.
USE PRACTICE_DB
GO
--Create PRODUCTS table
CREATE TABLE PRODUCTS
(
PRODUCT_ID INT
, PRODUCT_NAME CHAR(255)
, PRODUCT_CATEGORY CHAR(255)
, PRODUCT_PRICE FLOAT
, CURRENCY CHAR(5)
);
--Insert some values
INSERT INTO PRODUCTS (PRODUCT_ID, PRODUCT_NAME, PRODUCT_CATEGORY, PRODUCT_PRICE, CURRENCY) VALUES (1, 'Soap', 'Beauty Products', 25, 'GBP');
INSERT INTO PRODUCTS (PRODUCT_ID, PRODUCT_NAME, PRODUCT_CATEGORY, PRODUCT_PRICE, CURRENCY) VALUES (2, 'TV', 'Electronics', 500, 'GBP');
INSERT INTO PRODUCTS (PRODUCT_ID, PRODUCT_NAME, PRODUCT_CATEGORY, PRODUCT_PRICE, CURRENCY) VALUES (3, 'Laptop', 'Electronics', 900, 'GBP');
INSERT INTO PRODUCTS (PRODUCT_ID, PRODUCT_NAME, PRODUCT_CATEGORY, PRODUCT_PRICE, CURRENCY) VALUES (4, 'Hand cream', 'Beauty Products', 10, 'GBP');
INSERT INTO PRODUCTS (PRODUCT_ID, PRODUCT_NAME, PRODUCT_CATEGORY, PRODUCT_PRICE, CURRENCY) VALUES (5, 'Barbie', 'Toys', 56, 'GBP');
--Create product sales table
CREATE TABLE PRODUCT_SALES
(
SALES_ID INT
, PRODUCT_ID INT
, SALES_QUANTITY INT
, SALES_DATE DATE
);
--Insert some values
INSERT INTO PRODUCT_SALES (SALES_ID, PRODUCT_ID, SALES_QUANTITY, SALES_DATE) VALUES (101, 1, 5, '2023-09-01');
INSERT INTO PRODUCT_SALES (SALES_ID, PRODUCT_ID, SALES_QUANTITY, SALES_DATE) VALUES (102, 2, 1, '2022-12-01');
INSERT INTO PRODUCT_SALES (SALES_ID, PRODUCT_ID, SALES_QUANTITY, SALES_DATE) VALUES (103, 3, 2, '2022-11-01');
INSERT INTO PRODUCT_SALES (SALES_ID, PRODUCT_ID, SALES_QUANTITY, SALES_DATE) VALUES (104, 4, 3, '2023-09-15');
INSERT INTO PRODUCT_SALES (SALES_ID, PRODUCT_ID, SALES_QUANTITY, SALES_DATE) VALUES (105, 5, 5, '2022-07-01');
INSERT INTO PRODUCT_SALES (SALES_ID, PRODUCT_ID, SALES_QUANTITY, SALES_DATE) VALUES (105, 1, 6, '2021-12-17');
INSERT INTO PRODUCT_SALES (SALES_ID, PRODUCT_ID, SALES_QUANTITY, SALES_DATE) VALUES (105, 5, 7, '2023-05-01');
In order to find the Product sales details of a particular product category, we will write the following select query.
SELECT P.PRODUCT_NAME
, P.PRODUCT_PRICE
, P.PRODUCT_CATEGORY
, PS.SALES_QUANTITY
, PS.SALES_DATE
, P.CURRENCY
FROM PRODUCTS AS P
INNER JOIN
PRODUCT_SALES AS PS
ON P.PRODUCT_ID = PS.PRODUCT_ID
WHERE PRODUCT_CATEGORY = 'Electronics';We can now pack the above logic into a function, so we can reuse the function for different product categories.
-- REPORT ALL PRODUCT SALES INFORMATION FOR THE GIVEN PRODUCT CATEGORY
CREATE FUNCTION fnProductSales (@ProductCategory varchar(30))
RETURNS table
AS
RETURN
(
SELECT P.PRODUCT_NAME
, P.PRODUCT_PRICE
, P.PRODUCT_CATEGORY
, PS.SALES_QUANTITY
, PS.SALES_DATE
, P.CURRENCY
FROM PRODUCTS AS P
INNER JOIN
PRODUCT_SALES AS PS
ON P.PRODUCT_ID = PS.PRODUCT_ID
WHERE P.PRODUCT_CATEGORY = @ProductCategory
);Output:
In order to execute the function, we need to call them as below.
SELECT * FROM fnProductSales ('Beauty Products');The above function provides a table containing the Sales details of Beauty Products.
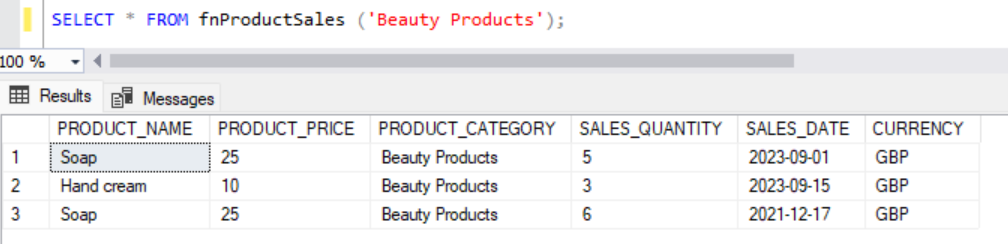
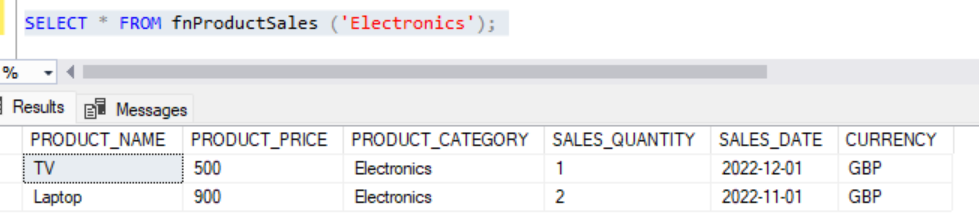
Similarly, we can call the same function for other products.
SELECT * FROM fnProductSales ('Electronics');
- Multi-Statement Table-Valued Functions (mTVF):
- These functions use a BEGIN…END block to define the function logic and return a result set in a table format.
- These functions store multiple statements in the function definition.
- Example : To report a list of alphanumeric sequence values, To generate calendar data etc.
Syntax:
CREATE FUNCTION <FUNCTION NAME>
(
-- Input parameters
@parameter1 data_type,
@parameter2 data_type,
-- ... (additional parameters if needed)
)
RETURNS @tableVariable TABLE
(
-- Columns definition for the table variable
)
AS
BEGIN
-- Function body with multiple statements
-- Populate the @tableVariable with data
RETURN;
END;
Example 1:
Generate a list of sequence numbers.
CREATE FUNCTION FN_GENERATE_SEQUENCE (@START_VALUE INT, @END_VALUE INT)
RETURNS @TABLEVARIABLE TABLE (Seq VARCHAR(30))
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @INDEX INT
SET @INDEX = @START_VALUE
WHILE @INDEX <= @END_VALUE
BEGIN
INSERT INTO @TABLEVARIABLE VALUES (@INDEX)
SET @INDEX = @INDEX + 1
END
RETURN
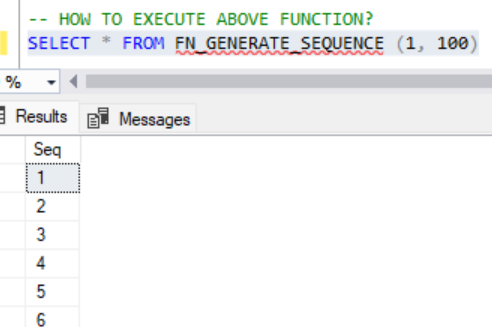
END To execute the above function, we need to execute the following statement.
SELECT * FROM FN_GENERATE_SEQUENCE (1, 100);The above function generates the sequence number from 1 to 100.
Output:
Example 2:
From the PRODUCTS table we created before, we can create a function to get highly priced products.
CREATE FUNCTION FN_HighlyPricedProducts
(
@priceThreshold FLOAT
)
RETURNS @result TABLE
(
Product_ID INT,
ProductName CHAR(50),
ProductCategory CHAR(50),
Product_Price FLOAT,
Currency CHAR(3)
)
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO @result
SELECT PRODUCT_ID,
PRODUCT_NAME,
PRODUCT_CATEGORY,
PRODUCT_PRICE,
CURRENCY
FROM PRODUCTS
WHERE PRODUCT_PRICE > @priceThreshold;
RETURN;
END;
To call the function, we execute the following.
SELECT * FROM FN_HighlyPricedProducts (500);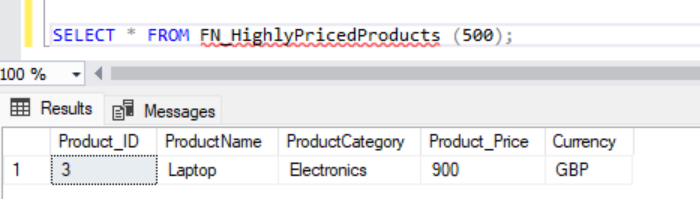
3. Aggregate functions:
- Operate on sets of values to return a single value.
- Examples include
SUM,AVG,COUNT,MIN,MAX, etc.
To learn more about aggregate functions, please follow this link. aggregate-functions-in-mssql
4. Windows functions:
- Perform calculations across a specified range of rows.
- Examples include
ROW_NUMBER,RANK,DENSE_RANK,LEAD,LAG, etc.
To learn more about Windows aggregate functions, please follow this link. windows-functions-in-mssql
5. Rowset functions:
OPENROWSET and OPENQUERY can be used to access data from external data sources.
To learn more about Rowset functions, please follow this link. rowset-functions-in-mssql
Summary:
- Functions are reusable code or objects with a predefined operation to perform a specific task.
- Functions can be system built in or user defined.
- Microsoft provides a variety of functions for a wide range of data operations.
- The functions are grouped into 5 categories in this blog. These are ,
- Scalar value returning functions
- Table valued functions
- Aggregate functions
- Windows functions
- Rowset functions
References:
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/functions/functions?view=sql-server-ver16#scalar-functions
- https://www.sqlite.org/lang_corefunc.html
- date-functions-in-mssql
- string-functions-in-mssql

