The MERGE statement in Microsoft SQL Server is a powerful and flexible command that allows you to perform multiple operations (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) in a single statement based on a specified condition.
It is very helpful when doing the ETL operations like UPSERTS (Inserts and Update) and data synchronization between the source and target data.
Basic Syntax:
MERGE target_table AS target
USING source_table AS source
ON <merge_condition>
WHEN MATCHED THEN
<update_statement>
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY TARGET THEN
<insert_statement>
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY SOURCE THEN
<delete_statement>;Example:
Let us see how merge statement works in real time.
For example, we often have different databases for development, test and production in real time, and the tables should be always synchronized. We can use MERGE statement to achieve this goal.
For that, let us first create some source and target tables to mimic the real time scenario.
USE TEMPDB
GO
--Creating the source table
CREATE TABLE SRC_SALES_SAMPLES
(
SALES_ID INT
, SALES_AMOUNT FLOAT
, SALES_DATE DATE
, SALES_TRACKING CHAR(255)
);
--inserting some values
INSERT INTO SRC_SALES_SAMPLES VALUES (1, 100.50, '2020-12-31', 'ABC400');
INSERT INTO SRC_SALES_SAMPLES VALUES (2, 200.00, '2018-09-30', 'REF123');
INSERT INTO SRC_SALES_SAMPLES VALUES (3, 300.75, '2022-12-31', 'GER345');
INSERT INTO SRC_SALES_SAMPLES VALUES (4, 400.90, '2020-12-15', 'TYU340');
INSERT INTO SRC_SALES_SAMPLES VALUES (5, 500.65, '2019-11-12', 'NUD903');
--Creating the target table
CREATE TABLE TRG_SALES_SAMPLES
(
SALES_ID INT
, SALES_AMOUNT FLOAT
, SALES_DATE DATE
, SALES_TRACKING CHAR(255)
);Output:
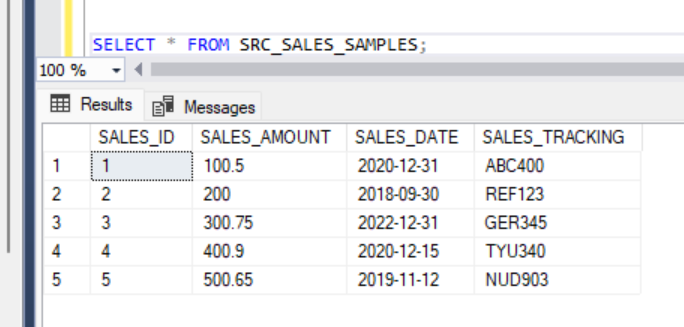
If we select from the source table, we will see the records inserted.
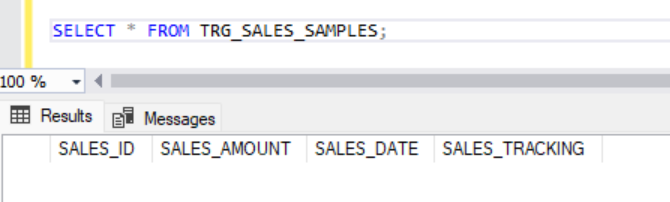
If we select from the target table, there will be no rows for now
Below, we can see the possibilties we have using MERGE statements.
1. Basic MERGE statement:
Let us create a Merge statement using our syntax given above.
MERGE INTO TRG_SALES_SAMPLES AS target_table
USING SRC_SALES_SAMPLES AS source_table
ON target_table.SALES_ID = source_table.SALES_ID
--When records are matched then we update
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET target_table.SALES_AMOUNT = source_table.SALES_AMOUNT
, target_table.SALES_DATE = source_table.SALES_DATE
, target_table.SALES_TRACKING = source_table.SALES_TRACKING
--When we dont't have the matching records in Target table, then we insert those records
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY TARGET THEN
INSERT ( SALES_ID
, SALES_AMOUNT
, SALES_DATE
, SALES_TRACKING)
VALUES ( source_table.SALES_ID
, source_table.SALES_AMOUNT
, source_table.SALES_DATE
, source_table.SALES_TRACKING)
--When the record from source table no longer exist, then delete it from the target table
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY SOURCE THEN
DELETE;Let us execute the above Merge statement and we will see that the INSERT statement has been executed, and the target table would have
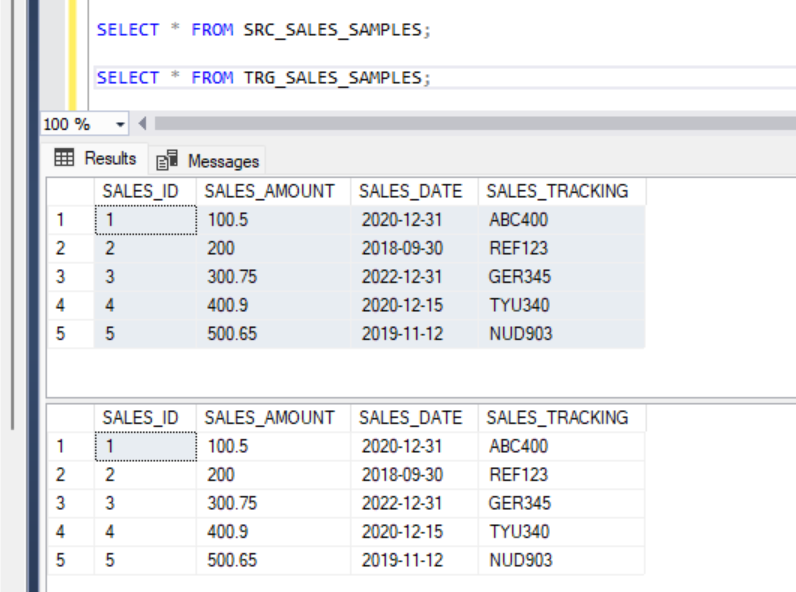
Now, if we select from the target table, we have the same number of rows as in the target table
Now let us modify a record in the source to see how the update in the MERGE statement works.
--Update an existing value in the source table
UPDATE SRC_SALES_SAMPLES SET SALES_AMOUNT = 2000.00 WHERE SALES_ID = 2;When we execute the above update statement, we will have a mismatch between source and table.
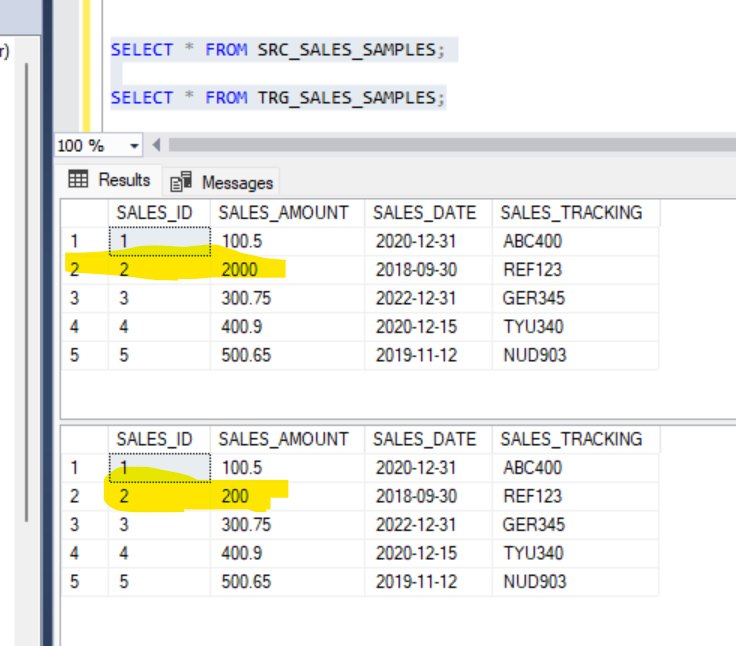
Now if we run the above MERGE statement, we get the record in the target table updated.
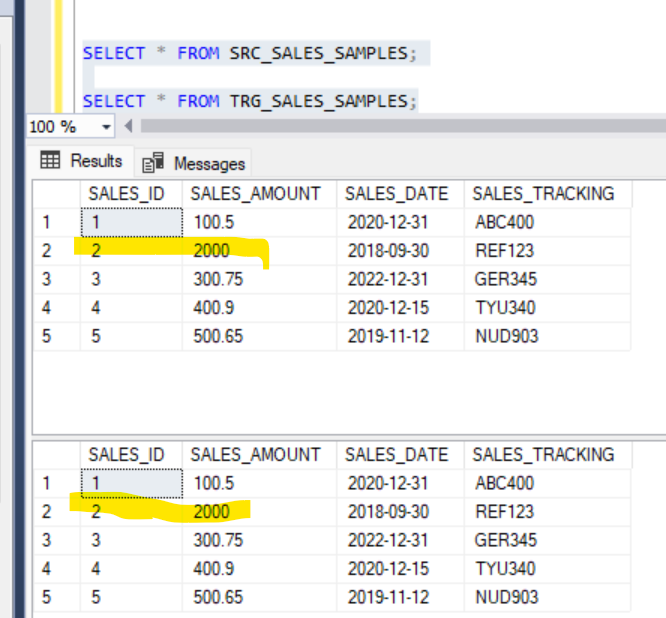
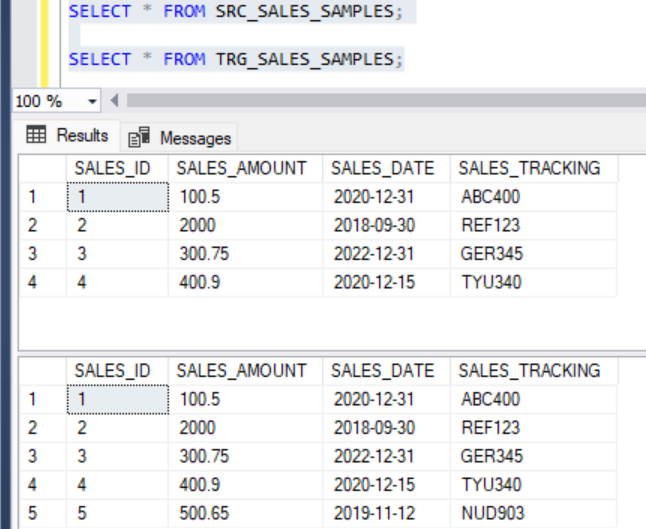
Now, let us delete a record from the source table and run the MERGE statement again.
--delete an existing value from the source table
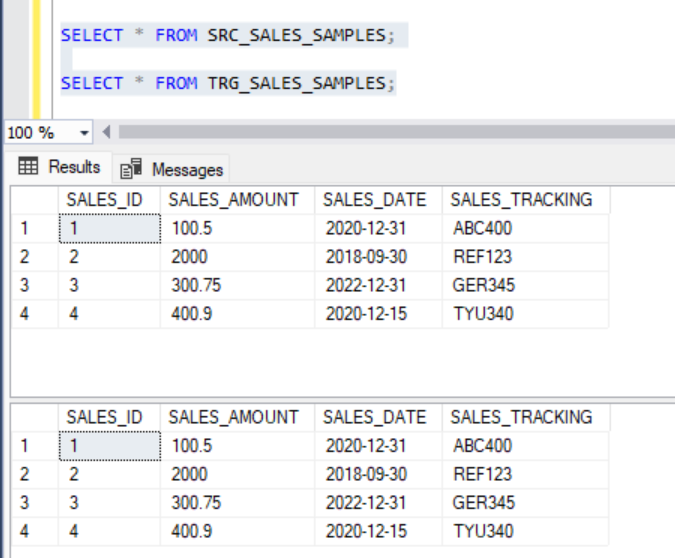
DELETE FROM SRC_SALES_SAMPLES WHERE SALES_ID = 5;Before running the MERGE statement, the source and target table looks like this,
After running the MERGE statement, we get the following result.
2. Using Additional Conditions:
If we want to filter the rows by adding additional conditions, we can also do that.
The below example shows how we can apply filters.
MERGE INTO TRG_SALES_SAMPLES AS target_table
USING SRC_SALES_SAMPLES AS source_table
ON target_table.SALES_ID = source_table.SALES_ID
--When records are matched then we update
WHEN MATCHED AND source_table.SALES_AMOUNT > 200 THEN
UPDATE SET target_table.SALES_AMOUNT = source_table.SALES_AMOUNT
, target_table.SALES_DATE = source_table.SALES_DATE
, target_table.SALES_TRACKING = source_table.SALES_TRACKING
--When we dont't have the matching records in Target table, then we insert those records
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY TARGET AND source_table.SALES_AMOUNT > 200 THEN
INSERT ( SALES_ID
, SALES_AMOUNT
, SALES_DATE
, SALES_TRACKING)
VALUES ( source_table.SALES_ID
, source_table.SALES_AMOUNT
, source_table.SALES_DATE
, source_table.SALES_TRACKING)
--When the record from source table no longer exist, then delete it from the target table
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY SOURCE THEN
DELETE;
Running the above query will result in inserting entries which are only having SALES_AMOUNT > 200 in the source table.
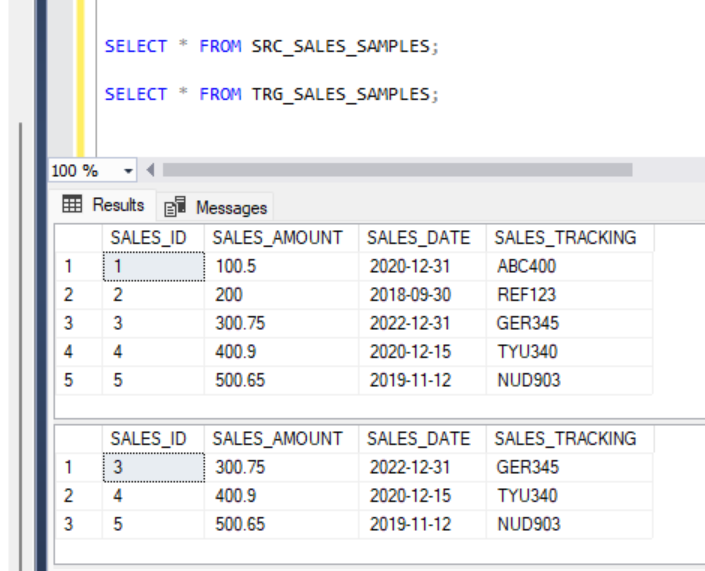
3. Logging Changes into an Audit Table:
- We can use the OUTPUT clause to log changes into an audit table.
To demonstrate it, let us create a sample Audit table.
CREATE TABLE AuditTable
(
Action VARCHAR(255)
, TargetSalesID INT
, TargetSalesValue FLOAT
, SourceSalesID INT
, SourceSalesValue FLOAT
);Perform some update and delete operations to trigger the audit logging.
--Update an existing value in the source table
UPDATE SRC_SALES_SAMPLES SET SALES_AMOUNT = 2000.00 WHERE SALES_ID = 2;
--delete an existing value from the source table
DELETE FROM SRC_SALES_SAMPLES WHERE SALES_ID IN (4, 5);Now run the following MERGE statement, with the OUTPUT clause added in the end.
MERGE INTO TRG_SALES_SAMPLES AS target_table
USING SRC_SALES_SAMPLES AS source_table
ON target_table.SALES_ID = source_table.SALES_ID
--When records are matched then we update
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET target_table.SALES_AMOUNT = source_table.SALES_AMOUNT
, target_table.SALES_DATE = source_table.SALES_DATE
, target_table.SALES_TRACKING = source_table.SALES_TRACKING
--When we dont't have the matching records in Target table, then we insert those records
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY TARGET THEN
INSERT ( SALES_ID
, SALES_AMOUNT
, SALES_DATE
, SALES_TRACKING)
VALUES ( source_table.SALES_ID
, source_table.SALES_AMOUNT
, source_table.SALES_DATE
, source_table.SALES_TRACKING)
--When the record from source table no longer exist, then delete it from the target table
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY SOURCE THEN
DELETE
--output the changes into an Audit table
OUTPUT $action AS Action
, inserted.SALES_ID AS TargetSalesID
, inserted.SALES_AMOUNT AS TargetSalesAmount
, deleted.SALES_ID AS SourceSalesID
, deleted.SALES_AMOUNT AS SourceSalesValue
INTO AuditTable (Action, TargetSalesID, TargetSalesValue, SourceSalesID, SourceSalesValue);We can see all the actions performed when we select from the AuditTable.
SELECT * FROM AuditTable;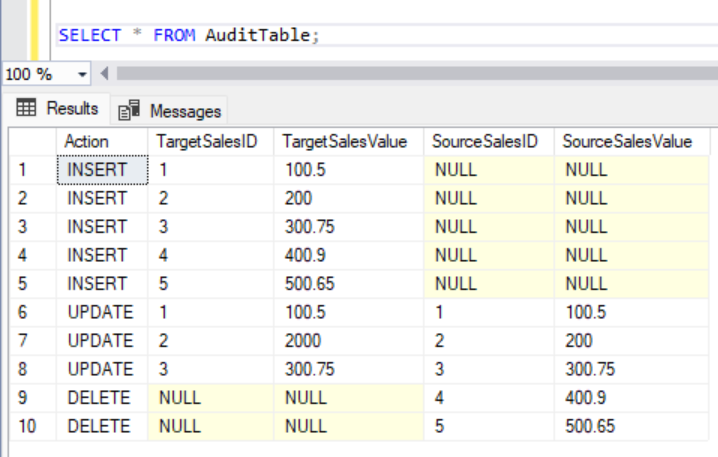
Summary:
- MERGE statements are used to perform ETL operations and UPSERTS effectively and gives us the opportunity to write INSERTS, UPDATES, and DELETES in a single statement.
- MERGE statements are often use in real time for source to target data synchronization.
- Always test the MERGE statement thoroughly, especially when dealing with complex conditions and multiple operations.
- Ensure that your ON conditions are well-defined and won’t result in unexpected matches.
- Consider using transactions to ensure atomicity when dealing with multiple operations.
- Be cautious when using the DELETE clause, as it removes rows from the target table.
- OUTPUT clause can be used to log into Audit tables.
- Use additional conditions to narrow down the exact rows to be merged.
- For best practices, always parameterize when inserting into the table.

