In Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL), there are various functions available for working with dates and times and there is a clear documentation on each of them on their website
Below are some commonly used date functions in every day data analysis, and reporting queries.
- To get the current date: GETDATE() , GETUTCDATE(), SYSDATETIME() and CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
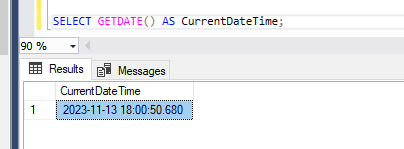
- We often need to get the current date and time when a particular database operation is made, like inserted date, modified date etc. In this case GETDATE() function becomes handy to get the current date and time.
SELECT GETDATE() AS CurrentDateTime;
SELECT GETUTCDATE() AS CurrentDateTimeUTC;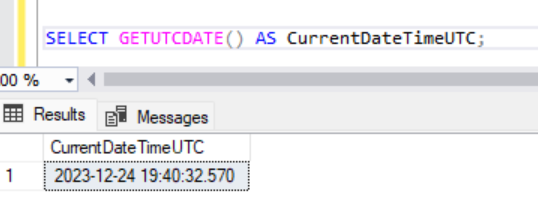
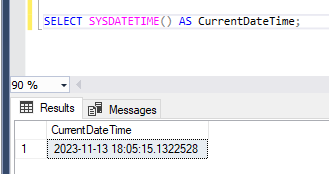
SELECT SYSDATETIME() AS CurrentDateTime;
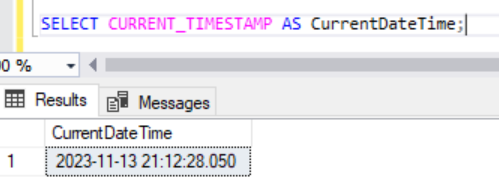
- Another way to see the current date and time is CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP AS CurrentDateTime;
2. To Format the dates into desired formats using FORMAT():
In real time, we need to often convert the format of a date based on the business requirements.
We can use FORMAT() for different datatypes. We can find in elaborate on using FORMAT() in Microsoft documentation.
Let’s see some of the most used cases here.
SELECT FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'MM/dd/yyyy') AS FormattedDate;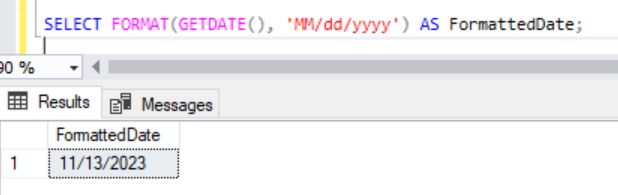
SELECT FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'yyyyMM') AS FormattedDate;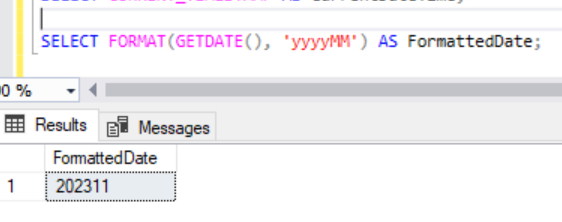
3. To extract part of dates: DATEPART(), YEAR(), MONTH(), DAY()
These functions are used to extract a specific part (e.g., day, month, year) from a date.
SELECT DATEPART(YEAR, GETDATE()) AS CurrentYear;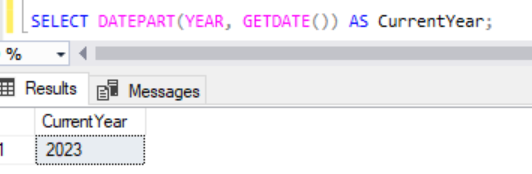
The same result can be obtained also by the following code,
SELECT YEAR(GETDATE()) AS CurrentYear;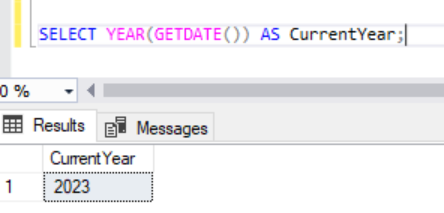
We can also get the MONTH and DAY of the year of any date we give.
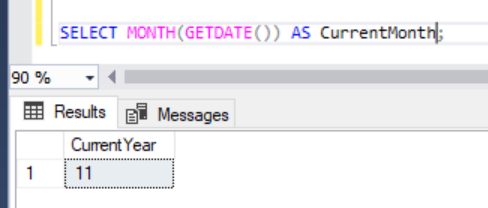
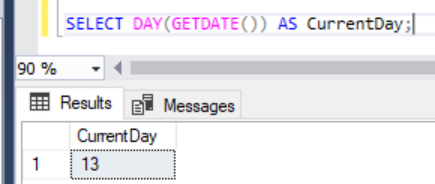
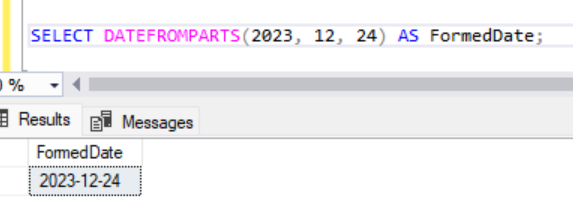
4. To form a date with seperate values: DATEFROMPARTS()
This function is helpful if you want to create a Date value by passing as parameters the year, month, and day as individual integer values.
Syntax:
DATEFROMPARTS ( year, month, day )
Example:
SELECT DATEFROMPARTS(2023, 12, 24) AS FormedDate;Output:
5. To calculate difference between 2 dates : DATEDIFF(), DATEDIFF_BIG()
DATEDIFF() is commonly used to find the difference between two dates or times in terms of a specified datepart, such as years, months, days, hours, minutes, seconds, etc. The result is an integer.
Syntax:
DATEDIFF ( datepart, startdate, enddate )
Example:
SELECT DATEDIFF(DAY, '2023-01-01' , '2023-12-24') AS DayDifference;
SELECT DATEDIFF(MONTH, '2023-01-01' , '2023-12-24') AS MonthDifference;
SELECT DATEDIFF(YEAR, '2023-01-01' , '2023-12-24') AS YearDifference;Output:
Executing the above 3 SQLs will give the following result.
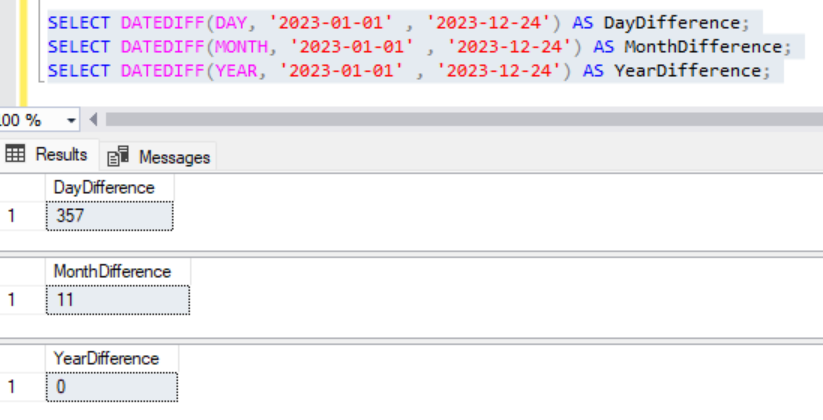
DATEDIFF_BIG()was introduced in SQL Server 2016 to address the limitation of DATEDIFF, which returns an integer. DATEDIFF_BIG returns a BIGINT value, allowing it to handle a larger range of date and time differences.
The syntax is same as DATEDIFF(), but here we can also find the time differences.
Example:
SELECT DATEDIFF_BIG(SECOND, '2023-01-01 00:00:00', '2023-12-24 23:59:59') AS SecondDifference;Output:
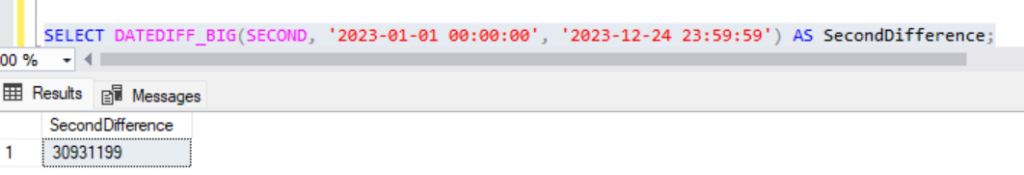
6. To perform date operations : DATEADD(), EOMONTH()
DATEADD() is used to add a specified time interval (or increment) to a date or time value. This function is helpful when you need to calculate a future or past date by adding or subtracting a certain number of units (such as days, months, years, etc.) from an existing date.
Syntax:
DATEADD (datepart, number, date)
Example:
--To check future date
SELECT DATEADD(MONTH, 5, '2023-12-24') AS FiveMonthsfromToday;
--To check previous date
SELECT DATEADD(YEAR, -5, '2023-12-24') AS BeforeFiveYearsfromToday;Output:
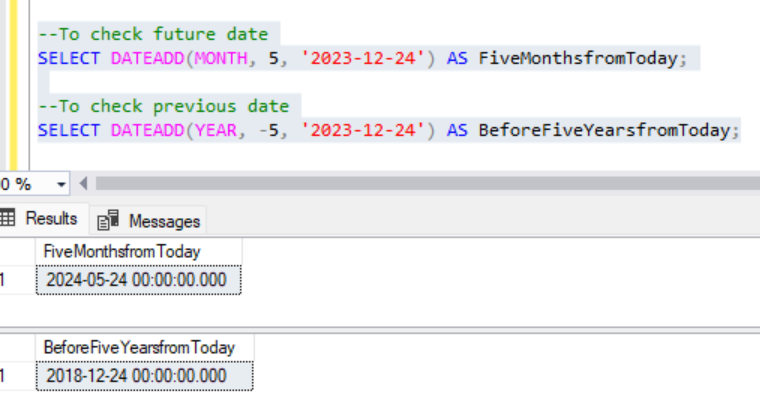
EOMONTH() is a function in Microsoft SQL Server that stands for “End Of Month.” It is used to return the last day of the month for a specified date. This function is particularly useful when you need to find the end date of a month, such as for financial or reporting purposes.
Syntax:
EOMONTH ( start_date [, month_to_add ] )
Example:
SELECT EOMONTH('2023-12-24') AS EndOfMonth;Output:
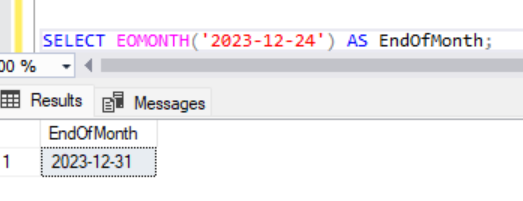
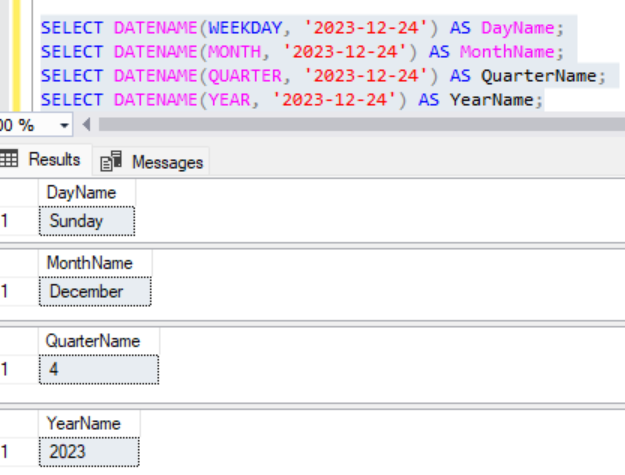
7. To get the date name: DATENAME()
DATENAME() is used to return a specified part of a date or time as a character string. You can use this function to extract the name of the day, month, or other date or time components.
Syntax:
DATENAME (datepart, date)Example:
SELECT DATENAME(WEEKDAY, '2023-12-24') AS DayName;
SELECT DATENAME(MONTH, '2023-12-24') AS MonthName;
SELECT DATENAME(QUARTER, '2023-12-24') AS QuarterName;
SELECT DATENAME(YEAR, '2023-12-24') AS YearName;Output:
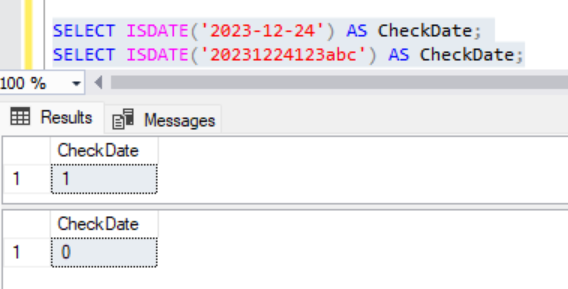
8. To check if the value is a date: ISDATE()
ISDATE() function is used to check whether an expression can be converted to a valid date. It returns 1 if the expression can be converted to a date; otherwise, it returns 0. This function is often used to validate whether a given string or value represents a valid date before attempting date-related operations.
Syntax:
ISDATE ( expression)Example:
SELECT ISDATE('2023-12-24') AS CheckDate;
SELECT ISDATE('20231224123abc') AS CheckDate;Output:
Executing the above 2 SQLs will result as,