In Microsoft SQL Server, sys.tables and sys.columns are system views that provide information about tables and columns within a database. These system views are part of the SQL Server system catalog, which contains metadata about database objects. Here’s an overview of each:
sys.tables:sys.tablesis a system view that contains information about tables within a database.It includes details about each table, such as the table name, object_id, schema_id, create_date, modify_date, and other metadata.You can usesys.tablesto query information about the tables in the database, including user-defined and system tables.
You can query sys.tables to obtain various details about each table in the database. Here are some of the key information you can retrieve:
- name: The name of the table.
- object_id: A unique identifier for the table within the database.
- schema_id: The identifier for the schema to which the table belongs.
- principal_id: The identifier of the principal (typically a user or role) that owns the table.
- parent_object_id: The identifier of the object that is the parent of this table (usually the schema).
- type: Indicates the type of the object, with a value of ‘U’ for user table.
- type_desc: A human-readable description of the object type, which will be ‘USER_TABLE’ for tables.
- create_date: The date and time when the table was created.
- modify_date: The date and time of the most recent modification to the table.
- is_ms_shipped: A flag indicating whether the table is a system table or a user-defined table.
- is_published: If the database is involved in replication, this column indicates whether the table is published.
- is_schema_published: Similar to
is_published, but specifically for schema replication.
These are the common columns you can query from sys.tables. You can use this information to understand the structure of tables in your database and perform various administrative and querying tasks. For example, you can use it to generate a list of user-defined tables, check when a table was created or last modified, or identify tables owned by specific database users or roles.
2. sys.columns:
sys.columnsis a system view that provides information about columns within tables in the database.It includes details such as the column name, object_id (referring to the table), column_id, system_type_id (data type), max_length, precision, scale, and other column-related metadata.You can usesys.columnsto query information about the columns in the tables.
You can query sys.columns to obtain various details about each column in the tables. Here are the key pieces of information you can retrieve:
- object_id: The unique identifier of the table to which the column belongs.
- name: The name of the column.
- column_id: The identifier for the column within the table.
- system_type_id: The system data type identifier for the column. You can use this to map to data types in
sys.types. - user_type_id: The user-defined data type identifier for the column. This can be used to link to user-defined data types.
- max_length: The maximum length of the column data type in bytes.
- precision: For numeric data types, this indicates the number of digits in the column.
- scale: For numeric data types, this indicates the number of decimal places.
- collation_name: The collation name for character and Unicode data types.
- is_nullable: A flag indicating whether the column allows NULL values (1 for NULLs allowed, 0 for NOT NULL).
- is_ansi_padded: A flag indicating whether ANSI_PADDING is on (1 for ON, 0 for OFF).
- is_rowguidcol: A flag indicating whether the column is a ROWGUIDCOL.
- is_identity: A flag indicating whether the column is an identity column (1 for identity column, 0 for not).
- is_computed: A flag indicating whether the column is a computed column (1 for computed column, 0 for not).
- is_filestream: A flag indicating whether the column is a FILESTREAM column (1 for FILESTREAM, 0 for not).
- is_replicated: A flag indicating whether the column is replicated (1 for replicated, 0 for not).
- is_sparse: A flag indicating whether the column is sparse (1 for sparse, 0 for not).
- is_column_set: A flag indicating whether the column is a column set (1 for column set, 0 for not).
These are the primary columns you can query from sys.columns. This information is valuable for understanding the structure of tables in your database and can be used for various administrative and querying tasks. For example, you can use it to identify the data type of a column, whether it allows NULL values, whether it’s an identity column, and more.
Using these system views, you can retrieve valuable metadata about tables and columns in your database. This information can be useful for tasks such as generating documentation, writing data dictionary reports, or performing data analysis. Additionally, you can filter and join these views with other system views to obtain more specific information about your database’s structure.
Keep in mind that accessing system catalog views may require appropriate permissions, typically administrative or database owner rights. Always exercise caution when working with system catalog views and ensure you have the necessary privileges.
Real Time use case scenario:
Often, we have a situation where the business needs a specific information. We might know the column name or sometimes we might not know the exact column name or the table name where the information resides. In that case, we can join sys.tables and sys.columns to find those tables.
For our practice, let us take the AdventureWorks Database
We have so many tables there and the business asks us for details about reviews.
We need to search all tables in this database for columns related to reviews.
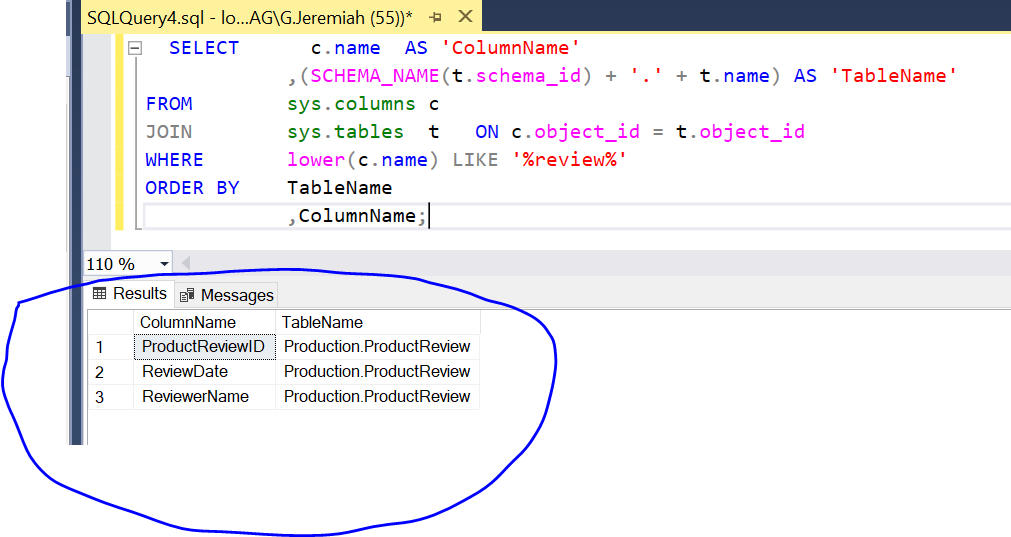
We use the below query to retrieve all tables and columns that has the value ‘review’ in it.
SELECT c.name AS 'ColumnName'
,(SCHEMA_NAME(t.schema_id) + '.' + t.name) AS 'TableName'
FROM sys.columns c
JOIN sys.tables t ON c.object_id = t.object_id
WHERE lower(c.name) LIKE '%review%'
ORDER BY TableName
,ColumnName;Executing the above query will give the following result.