In stored procedures, variables are used to store and manipulate data within the procedure. It is a placeholder to store data in memory.
In real time, we often have situations where we need to run a procedure frequently. It is not a good practice to open the procedure everytime and change the conditions of the query. So, we need to use variables.
The syntax might vary depending of the database. In MSSQL Server, we can use the following way to use variable inside stored procedure.
Syntax:
-- Declare variables
DECLARE @VariableName DataType;
-- Set a value to the variable
SET @VariableName = 'SomeValue';
-- Use the variable in a query
SELECT * FROM TableName WHERE ColumnName = @VariableName;
@VariableNameis the name of the variable.DataTypeis the data type of the variable (e.g., INT, VARCHAR, etc.).SETis used to assign a value to the variable.- You can then use the variable in your SQL queries.
For MySQL, the syntax is similar:
-- Declare variables
DECLARE VariableName DataType;
-- Set a value to the variable
SET VariableName = 'SomeValue';
-- Use the variable in a query
SELECT * FROM TableName WHERE ColumnName = VariableName;
For PostgreSQL:
-- Declare variables
DECLARE VariableName DataType;
-- Set a value to the variable
VariableName := 'SomeValue';
-- Use the variable in a query
SELECT * FROM TableName WHERE ColumnName = VariableName;
Remember to replace DataType, VariableName, TableName, and ColumnName with your actual data types, variable names, table names, and column names. If you’re using a specific DBMS, it’s always a good idea to refer to its documentation for the exact syntax and rules.
Real time use case:
Now the fun part, Let’s put into practice this concept of using variables inside a stored procedure.
Step 1: Source
For practice, I use the AdventureWorks2019 database and [Production].[WorkOrder] table.

Step 2: Example Scenario and Query
Lets say that we need to know the count of Stocks that are due in the year 2011
The SQL to get this requirement is,
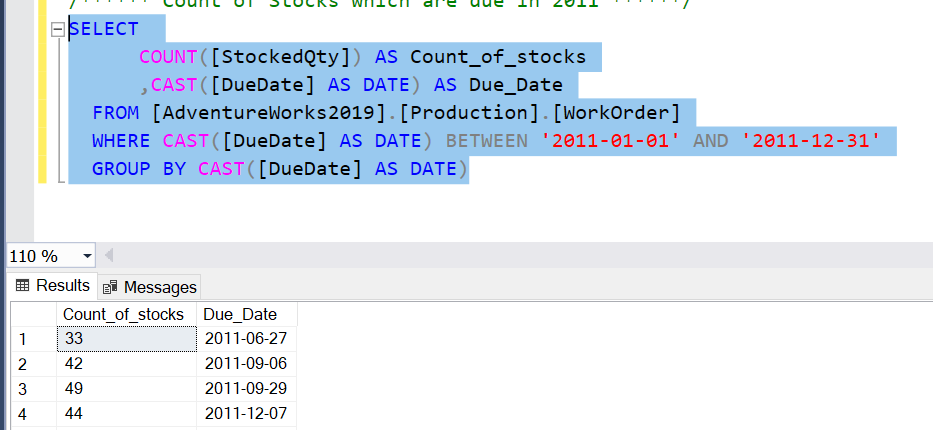
SELECT
COUNT([StockedQty]) AS Count_of_stocks
,CAST([DueDate] AS DATE) AS Due_Date
FROM [AdventureWorks2019].[Production].[WorkOrder]
WHERE CAST([DueDate] AS DATE) BETWEEN '2011-01-01' AND '2011-12-31'
GROUP BY CAST([DueDate] AS DATE);The above query produces the following result
Step 3: Use Variables
Now, instead of hardcoding the dates, we can use variables for the start and end dates.
DECLARE @START_DATE DATE;
SET @START_DATE = '2011-01-01';
DECLARE @END_DATE DATE;
SET @END_DATE = '2011-12-31';
SELECT
COUNT([StockedQty]) AS Count_of_stocks
,CAST([DueDate] AS DATE) AS Due_Date
FROM [AdventureWorks2019].[Production].[WorkOrder]
WHERE CAST([DueDate] AS DATE) BETWEEN @START_DATE AND @END_DATE
GROUP BY CAST([DueDate] AS DATE);Step 4: Create procedure and pass variable as parameter
To further make it reusable, we can put the query inside a stored procedure and pass the variable as parameter.
CREATE PROCEDURE NO_OF_DUE_STOCKS
@START_DATE DATE,
@END_DATE DATE
AS
BEGIN
SELECT
COUNT([StockedQty]) AS Count_of_stocks
,CAST([DueDate] AS DATE) AS Due_Date
FROM [AdventureWorks2019].[Production].[WorkOrder]
WHERE CAST([DueDate] AS DATE) BETWEEN @START_DATE AND @END_DATE
GROUP BY CAST([DueDate] AS DATE)
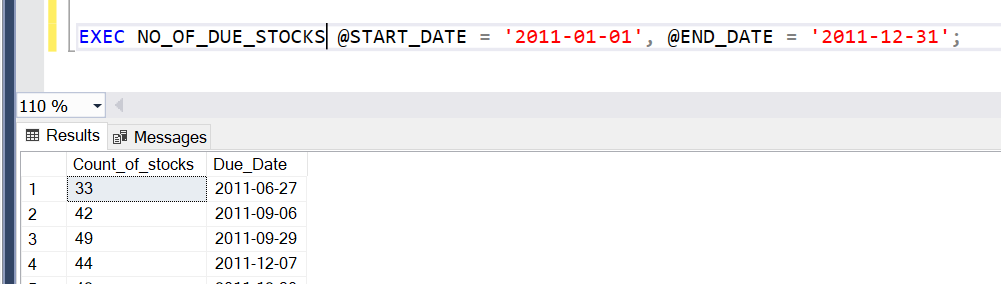
END;To execute the procedure, we should use EXEC command as follows,
EXEC NO_OF_DUE_STOCKS @START_DATE = '2011-01-01', @END_DATE = '2011-12-31';Executing the procedure will give us the same result as the SQL query
Conclusion:-
We can write a simple SQL, but applying the best practices by using variables and procedures saves us time for subsequent and frequent runs.
It is also easier to make changes in one place, rather to update values in multiple queries, which can cause errors.

